AI for Preference Learning: Sentiment, Comparison, and Recommendation
Artificial Intelligence or AI is pervading many aspects of our lives, influencing the array of options we encounter and changing the way we make decisions. Preference learning is a branch of machine learning that focuses on extracting preference signals from data and utilizing them to make predictions based on user preferences. This is one of the research areas being actively pursued by Preferred.AI.
Our recent research results (2 full papers and 1 tutorial) would be presented at AAAI-19, one of the two major international conferences on AI. In preparation for these presentations, we held a research workshop featuring three talks by our members on 21 January 2019.

Tuan started the ball rolling with VistaNet, a multimodal sentiment analysis technique that leveraged images within a review as a visual attention mechanism to support the textual features in predicting the sentiment of the review. This would be useful in sensing user preferences especially as our phones are now ever-present cameras with which we can express our preferences.
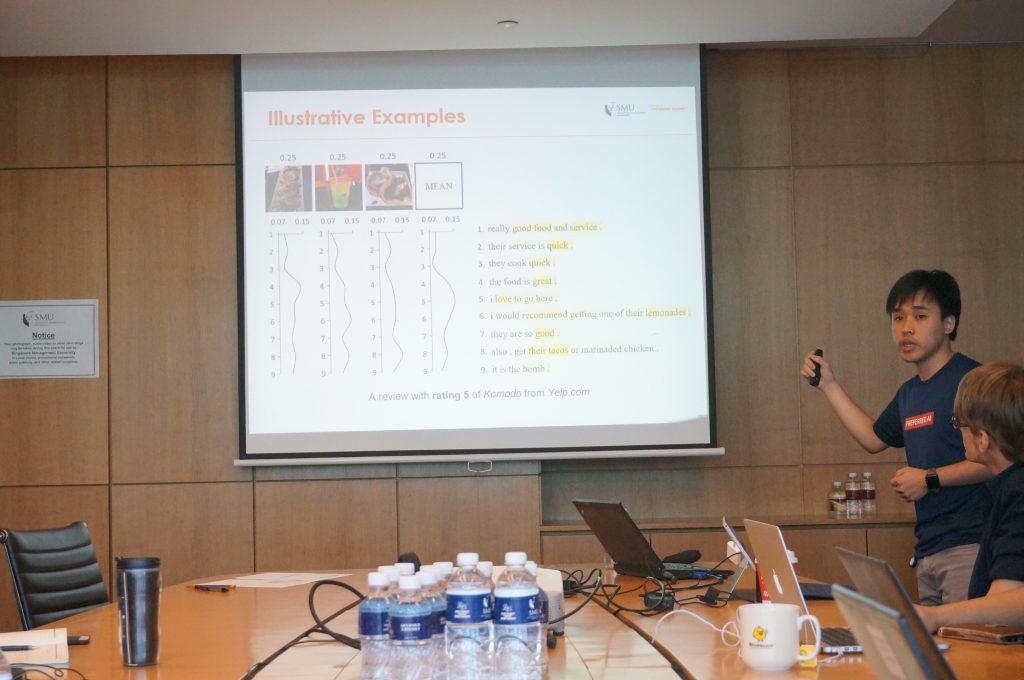

Max weighed in with CompareLDA, pointing out the utility of comparative analysis of textual passages or documents in learning what made a document ranked higher than another. For instance, this could help reveal why a product (e.g., camera) is preferred over another based on their reviews.

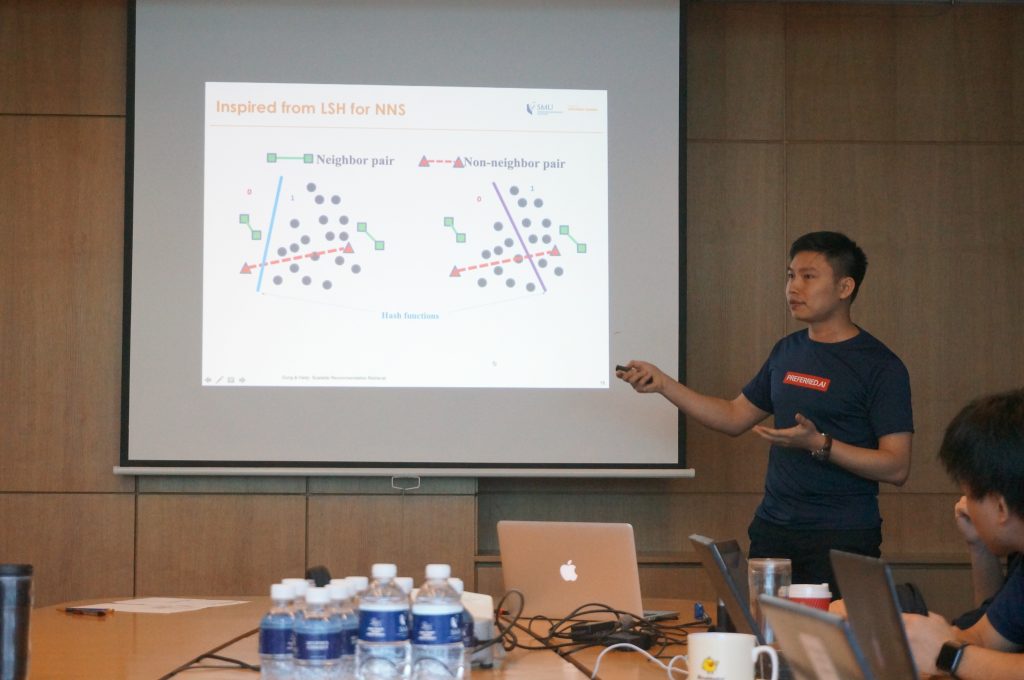
Andrew rounded out the workshop with a mini-tutorial on scalable recommendation retrieval, emphasizing the need to consider not only the accuracy of recommendations but also the speed at which they were delivered to the users. This was a subset of a longer tutorial he would be delivering at AAAI-19.
The workshop was a success, attended by almost 30 students and staff from the School of Information Systems. We’re grateful to the the Postgraduate Research Office that sponsored the event as a DIY activity by SMU PhD students.





